
Overview of Subsystems
SAMAN's comprehensive IT infrastructure is well beyond a simple track and trace record-keeping system. Our solution literally encompasses all stakeholders of Pharma supply chains (i.e. pharmacists, wholesalers, Manufacturers, governmental organizations) and brings them together in a single unified solution. Below is a concise overview of the main constituent parts of the system. However, it should be noted that some parts such as payment subsystem, financial infrastructure, etc have been omitted for the sake of simplicity.
Subsystems
Concise overview of the main constituent parts of the system
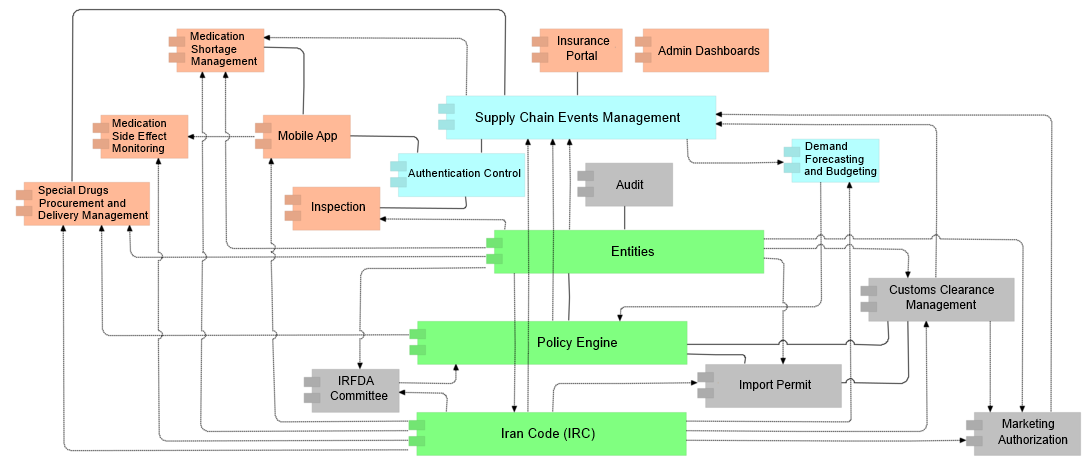
Marketing Authorization
This is the last step for the imported/domestically produced health related products before serialization.
Legally produced/imported products which are stored in warehouses with previously known GLNs are at times subject to additional safety related procedures such as sampling before they can enter the market.
Said operations are handled via the "marketing authorization" subsystem.
Customs Clearance
Customs Clearance system consults the Import Permit subsystem before consignments of health related products are allowed to enter the country.
Import Permit
Import permits are granted based on the data received from three other subsystems : Entities, IRC , and Policy Engine.
Demand Forecasting
Future demand forecasting is realized by relying on historical data (Event Management subsystem), ratified policies, and data on current production/import volumes.
Insurance Portal
Insurance companies have a dedicated portal through which they are allowed to interact with the system.
Admin Dashboards
Events Management
This is the hub where all the data from supply chain activities is gathered and analyzed thereby, creating a comprehensive map of distribution and consumption.
Audit
All the entities registered in the system are regularly audited with respect to processes and practices to insure absolute compliance with the IRFDA guidelines and regulations.
Entities
Entities is a registry of all the companies and their CEOs and technical directors which are somehow involved in the Pharma supply chain. Moreover, it includes the location of said companies, facilities, warehouses, and branches; each identified by a unique GLN.
Policy Engine
Policy engine takes in data and policies from the IRFDA committee as input and produces responses to policy related questions.
Iran Code(IRC)
Every health related product is assigned a 16 digit code knows as the IRC. assigned IRCs vary based on a number of factors. mainly :
product type, manufacturing company, packaging , importer company. therefore, two identical products produced by the same manufacturer would require two different IRCs even if their packaging is in any way different.
Authentication Control
Authentication control system responds to queries regarding the authenticity of products.the response generated by the system may vary depending on the credentials of the user viewing it.
a log of the queries and generated responses thereto are kept within the system which is utilized as the basis for prompt actions in case of need as well as future use in analysis.
Mobile App
Authentication could be carried out by the customer at the point of dispensing using the TTAC mobile application.there are also a number of additional handy features included within the app.
Learn more
Inspection
Aside from authentication by customers, inspection at the level of point of dispensing might be carried out by IRFDA officers during planned or surprise visits to pharmacies and hospitals.
results of such inspections are gathered via a dedicated app and fed to the authentication control system.
Shortage Management
The reports of shortage received are first validated by comparing them to distribution/consumption patterns generated by other sub systems.
Each validated case of shortage raises a flag so the appropriate action could be taken.
Side Effects
Reported side effects are gathered and analyzed.
Special Drugs
A handful of very expensive drugs which are used to treat special diseases are procured and delivered directly to the patient using this system .
The cost of said medicine is covered almost entirely by the IRFDA, even if the patient doesn't have insurance coverage .
IRFDA Committee
The medicine committee is responsible for regulation of the market.this task is carried out by developing a range of policies such as import quota, market authorization, required standards and Lab tests, etc.
said policies are fed into the policy engine through a dedicate portal.
A sample case scenario for importing a new medicine:
Company "A" wants to import a type of medicine called "example medicine(EM)" which is a type of painkiller manufactured by the company "B".
Company "A" has been active on the market for some time and therefore, it is already registered in the "Entities" subsystem. that is to say, all the relevant information
regarding the company such as key people(CEO and technical director),location ,branches, warehouses, etc, are already verified and registered in the system.
Some products form company B have previously been imported to the country. moreover, similar products to EM from other manufacturers have previously
been imported as well. but, EM medicine manufactured by the company "B" is unprecedented in the Iranian market. Since IRC is a very specific coding system,
company "A" would be required to submit the necessary documents and ask for a unique new IRC to be generated for EM medicine ,
manufactured by company "B" , with previously defined shape and packaging. assigining an IRC to a product signifies that IRFDA recognizes
the compliance of said product and the manufacturing company with the required criteria.
Once an IRC is generated and assigned to the product, the company may submit their request for importing. One thing to consider is that assigning a unique IRC to a
product ,though necessary , does not serve as the absolute permission for importing the product as each case of import would be also subject to permissions set by the policy engine.
for each import request, the "import permit" subsystem processes the requests and grants permission after consulting with the policy engine. this subsystem would later on inform the
customs clearance system once the product has reached ashore and is waiting to be released.
denying import permission for a valid IRC by the policy engine could happen due to a
number of reasons. some examples are as follows :
- there is a quota on imported painkillers which has already been reached.
- importing medicine from a specific country is currently prohibited until further notice.
etc .
as the products are cleared through customs, they are stored in a warehouse with previously known GLN and storage conditions. at this stage the company
is not yet authorized to sell .
before the company could hand the products to a wholesaler, it should ask for permission from "Marketing Authorization" subsystem which might involve some additional
safety related procedures. For instance, some random sampling and lab tests might be required.
Once the marketing authorization is granted, the products (each affixed a label containing batch No, Expiration date, and a unique serial number) embark on their
journey down the supply chain usually through a wholesaler.
